Blockchain VS Hashgraph
 The recent popularity of blockchain technology, stemming mainly from its utilization in a vast range of processes. Depending on the context, Blockchain may signify a distributed computer network, software supporting operations of the computers in the distributed system, or market of distributed applications and networks. Such flexibility of definitions is an outcome of the concept's applications in various industries and fields.
The recent popularity of blockchain technology, stemming mainly from its utilization in a vast range of processes. Depending on the context, Blockchain may signify a distributed computer network, software supporting operations of the computers in the distributed system, or market of distributed applications and networks. Such flexibility of definitions is an outcome of the concept's applications in various industries and fields.
Blockchain has a delivered ledger technology at its core. In spite of the proven capability of Blockchain, it still has its restrictions on speed, synchronicity, scalability, which is the primary reason for several companies and individuals searching for alternatives. Hashgraph is one of those abilities for solutions. The Hashgraph has a decentralized data structure that provides a higher level of speed and reliability compare to Blockchain. Thus it is vital to assess the ability of the new technological concept.
Hashgraph vs Blockchain:
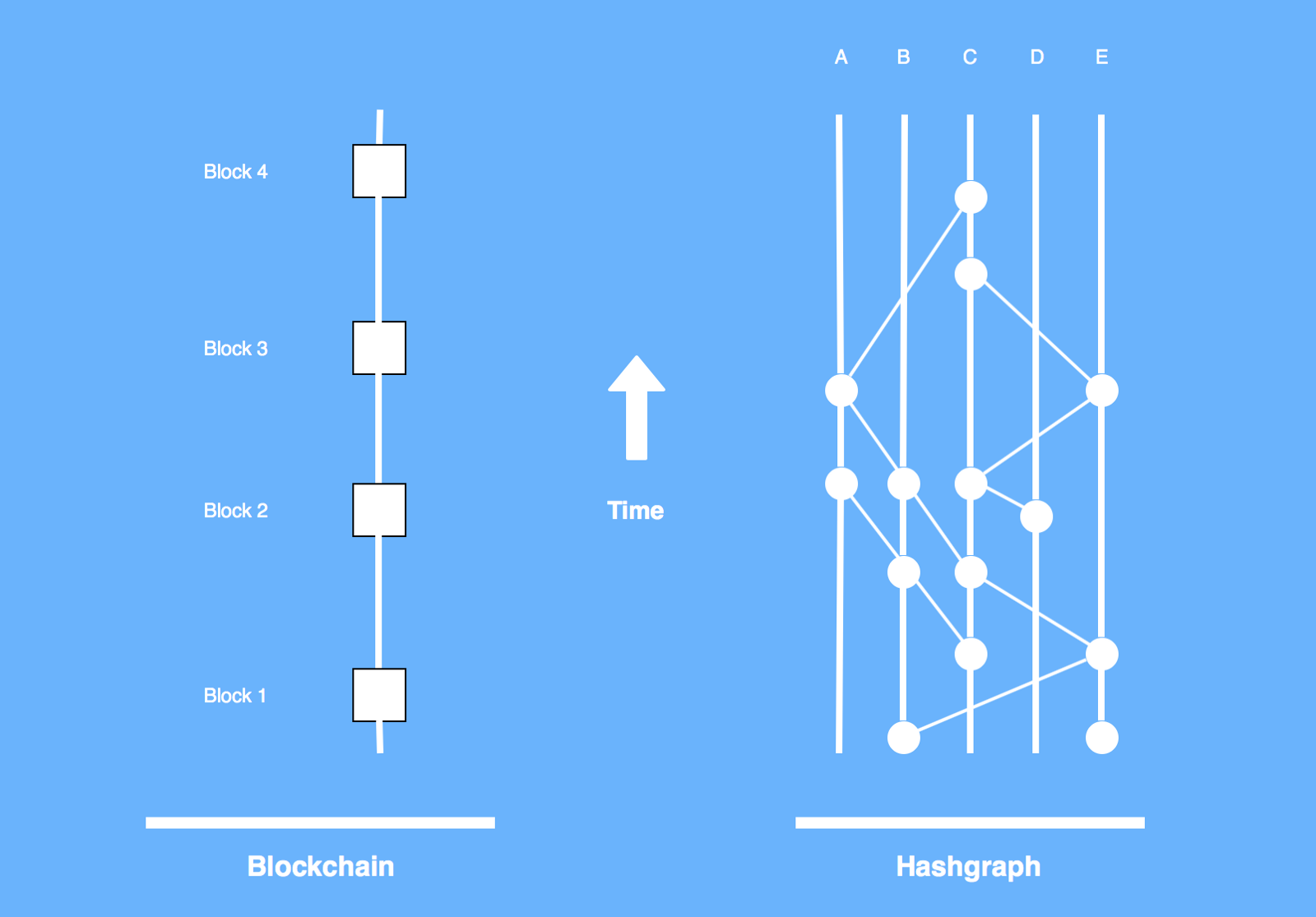
It is possible to compare Hashgraph and Blockchain based on three main aspects, data structure, namely data storage and protocols. Blockchain signifies the storage of transaction records in a block, timestamp, including current hash, as well as the transaction from the previous block. Hashgraph stores data in the form of containing timestamps, events, and transactions with the common hashes. It is also possible to see past transactions in a graph.
The process of data structure differs between Hashgraph and Blockchain. Blockchain technology adopts nodes authorized for adding blocks to the chain of transactions. Hashgraph technology needs communication of the nodes, sending the information through the connections recorded in a graph. So, Blockchain keeps data in chronological order, where Hashgraph provides parallel transactions.
Blockchain uses two main consensus protocols, namely Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Work (PoW), and their variations. PoW protocol implements mining over a series of complex mathematical calculations.
The protocol allows the miners to solve the problems.
The same process provides the validation of blocks through security algorithms.
The protocol needs substantial amounts of energy and time. The PoS protocol signifies the selection of the new block creators based on their stake or wealth. Unlike the PoW, PoS does not allow the rewards, as miners ordinary charge fees for transactions. The significant benefits of PoS protocol are its efficiency and higher speed. But, it is more centralized and less secure from the security point of view.
Hashgraph adopts Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT) or gossip about gossip protocol.
The protocol is the focal for the system’s security and resistance to fraud. The ABFT protocol doesn't need extra nodes for its execution while occurring in three steps. First, the protocol separates the process into rounds with each round create after the event can connect at least 67% of the first events within the series to 67% of the node group. Second, the formation of the new round signifies voting of the first several nodes to validate the data kept in the first row of the previous series. Such a process requires a connection between the considered nodes. Third, the group of the 3rd round node answers occurs using the 4th round nodes for the achievement of the consensus.
Both technologies are DDoS resilient and ACID-compliant (where ACID stands for atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability). They depend on encryption of interaction and communication with hashes, as well as cryptographic signatures to prevent theft. Besides, adherence to security standards protects private information. The protocol utilized by Hashgraph precludes the influence of a single user or a small group of users on an entire system. The result depends on the confirmation of the history, validity, and information of the event.








Add comment